Idarubicine
L'idarubicine ou 4-déméthoxydaunorubicine est un anticancéreux de type anthracycline. Elle s'insère dans l'ADN et l'empêche de se dérouler en interférant avec l'enzyme topoisomérase II. C'est un analogue de la daunorubicine, mais l'absence de groupe méthoxy accroît sa Liposolubilité et son absorption cellulaire[3] .
| Idarubicine | |
 | |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
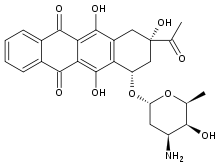
| Nom UICPA | (1S,3S)-3-acétyl-3,5,12-trihydroxy-6,11-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydrotétracén-1-yl 3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxo-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranoside |
| No CAS | |
| Code ATC | L01 |
| PubChem | 42890 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule brute | C26H27NO9 [Isomères] |
| Masse molaire[1] | 497,4939 ± 0,0256 g/mol C 62,77 %, H 5,47 %, N 2,82 %, O 28,94 %, |
| Écotoxicologie | |
| DL50 | 16 mg/kg (souris, oral)[2] 4 mg/kg (souris, i.v.)[2] 3 mg/kg (souris, i.p.)[2] |
| LogP | 2.100 (octanol/eau)[2] |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
Notes
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) « Idarubicin » sur ChemIDplus.
- Package insert
- Portail de la pharmacie
- Portail de la chimie
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.