Dextroamphétamine
La dextroamphétamine, commercialisée comme sulfate sous le nom de Dexedrine, est un médicament servant à traiter l'hyperactivité ou la narcolepsie ainsi que l'hypersomnie. C'est l'énantiomère S dextrogyre de l'amphétamine. La dextroamphétamine a également des propriétés neurostimulantes.
| Dextroamphétamine | |
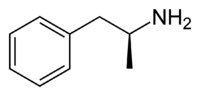 | |
| (S)-dextroamphétamine | |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | (+)-(S)-1-phénylpropan-2-amine |
| Synonymes |
Dextroamphétamine |
| No CAS | (D) ou S(+) |
| No ECHA | 100.000.103 |
| No EC | 200-112-1 |
| Code ATC | N06 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule brute | C9H13N [Isomères] |
| Masse molaire[1] | 135,2062 ± 0,0083 g/mol C 79,95 %, H 9,69 %, N 10,36 %, |
| Propriétés physiques | |
| T° fusion | < 25 °C |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- Portail de la médecine
- Portail de la chimie
- Portail de la pharmacie
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.